1. What is UL Certification and Why is it Important?
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) is a leading third-party safety certification organization worldwide. Founded in 1894 in Chicago, UL is widely recognized across North America, Canada, Europe, and many international markets.
With the mission of making the world safer for both workers and consumers, UL certification is considered a global symbol of quality, setting industry standards that must be followed when innovating products and conducting rigorous safety testing.
In international trade, UL has become a “passport” that helps products easily enter markets such as the U.S., EU, Canada, and other countries requiring safety certification.
In the electronics industry, UL standards serve as a foundational system, shaping safety and quality requirements across the entire supply chain and often determining the survival of products in global markets.
Major retailers such as Walmart, Target, Best Buy, Home Depot, and Lowe’s typically require UL certification for electrical products. With such strict testing and compliance requirements, what benefits does UL bring?
2. Why Should You Have UL Certification or Buy UL-Certified Products?
Benefits for Businesses
- Compliance: UL helps companies prove that their products meet safety standards and regulatory requirements.
- Market Expansion: UL-certified products are more easily accepted in the U.S. and many other countries, opening export opportunities.
- Brand Reputation: UL is a trusted certification mark, enhancing brand image, building trust with partners and customers, and creating a competitive advantage.
- Reduced Legal Risks: Having UL certification minimizes the risk of lawsuits or insurance issues related to product safety.
Benefits for Consumers
- Safety: Buying UL Listed or UL Certified products ensures they have undergone strict safety testing, reducing risks of fire, explosion, or malfunction.
- Trustworthiness: The UL mark is a sign of quality, helping consumers choose confidently among different brands.
- Legal Protection: In case of incidents, UL-certified products are often covered by insurance and legally recognized, protecting consumer rights.
3. Types of UL Certification
UL certification includes various services designed to meet specific needs, such as:
- Personnel Certification: UL ensures your workforce meets industry standards.
- Product Certification: UL verifies that your products comply with all necessary regulations.
- Facility Certification: UL confirms that your physical sites comply with safety and operational standards.
- Process Certification: UL validates that your processes are effective and compliant.
- System Certification: UL assesses and certifies your management systems to achieve optimal performance.
Comparison: UL Listed vs. UL Recognized
| Criteria | UL Listed | UL Recognized |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Certification for finished products that UL has tested and confirmed to meet safety requirements. | Certification for materials, components, or sub-assemblies evaluated by UL according to a specific standard. |
| Scope of Application | Consumer electronics, household appliances, machinery, industrial equipment, etc. | PCB (Printed Circuit Boards), sensors, labels, printing materials, adhesives, wires, components, insulation materials, etc. |
| Purpose | Ensures the finished product is safe for end-use. | Ensures components or materials are suitable for use in UL-certified products. |
| Typical Examples | Laptops, adapters, household appliances, meters, UPS units, etc. | UL969 labels, UL94 materials, adhesives, UL758 wiring, UL746C insulation materials, etc. |
| Marking | UL Listed symbol (circle or square). | UL Recognized Component symbol (“UR”). |
| Intended Users | Manufacturers of finished products (OEMs). | Component, material, or sub-assembly manufacturers supplying OEM/EMS. |
| Supply Chain Impact | Products can be sold directly into the U.S. – Canada market. | Components are approved for use in UL Listed products, accelerating OEM qualification. |
| Testing Level | Comprehensive testing: electrical, mechanical, thermal, and user safety. | Specialized testing based on the relevant standard (e.g., label durability, heat resistance, insulation performance). |
4. UL Standards and Applicable Scope
Applicable Scope
- Electrical & Electronics Industry: PCB, electronic devices, components such as wires, sockets, office equipment, industrial machinery, etc.
- Labeling & Printing Industry: product labels, ribbons, adhesive materials.
- Materials Industry: plastics, polymers, rubber, flame-retardant materials.
- Information Technology & Telecommunications: computers, networking equipment, audiovisual devices.
- Consumer Goods: household appliances, kitchen equipment, lighting products, furniture.
Common UL Standards Related to the Electrical & Electronics Industry
Standards issued by UL Standards & Engagement are categorized by product characteristics and application fields. Some typical standards include:
- UL 969 – Label & Ribbon Standard: ensures labels, tags, and ribbons on components, machinery, or factories do not peel or fade under harsh conditions (temperature, chemicals, humidity).
- UL 94 – Flammability Standard for Plastics: classifies the fire resistance of plastics, commonly applied to electronic devices and components.
- UL 924: Standard for Emergency Lighting and Electrical Equipment.
- UL 508: Industrial Equipment Standard, applies to control panels and industrial electrical equipment (now replaced by UL 60947-4-1).
- UL 50: Enclosures for Electrical Equipment.
- UL 244B: Controllers for Field-Installed or Connected Equipment.
- UL 61010-1: Safety Standard for Electrical Equipment used in Measurement, Control, and Laboratories.
- UL 1558: Low-Voltage Metal-Enclosed Switchgear.
- UL 698: Industrial Control Panels for Hazardous Locations.
- UL 1449: Surge Protective Devices (SPD).
- UL 1977: Electrical Connectors.
5. Case Study: UL Certification Helps Businesses Export with Confidence and Build Strong Brand Trust
Background
An electronics manufacturing plant in Vietnam was preparing to export products to the U.S. The main products included power supplies and electronic circuit boards for office equipment. These products carry high risks of fire and electrical hazards, requiring strict safety certification.
Challenges
- Without UL certification, products would struggle to gain acceptance from U.S. distributors.
- Legal risks: products could be rejected at customs or recalled if incidents occurred.
- International customers often prioritize UL Listed products, as this is seen as a “quality assurance mark” for safety.
Solution
The factory decided to apply for UL certification for its power supply line.
- Testing process: UL conducted flammability tests (UL94), mechanical durability, thermal endurance (UL 62368-1), and label durability (UL969).
- Result: the products met standards and were granted UL Listed certification.
- Application: the UL logo was printed directly on products and packaging, making it easy for customers to identify.
Business Outcomes
- Confidence in exporting, without fear of rejection at customs.
- Enhanced brand reputation, enabling contracts with major international partners.
- Reduced legal risks and product insurance costs.
This case study demonstrates that UL certification is not just a document but a “shield” protecting both businesses and consumers. Companies gain peace of mind in operations, while consumers feel secure in usage.
6. Process to Obtain UL Certification
Step 1: Register for UL Certification
Businesses must visit UL’s official website, under the “Contact Us” section. Here, they fill out a form with basic information about the product requiring certification.
This step initiates the process, allowing UL to understand the needs and scope of testing.
 Fill out the UL certification registration form directly on the UL.com website (source: UL Solutions).
Fill out the UL certification registration form directly on the UL.com website (source: UL Solutions).After registration, a UL consultant will contact you. You will receive detailed instructions and prepare to send product samples to UL’s laboratory.
Packaging must be done carefully to ensure the samples are not damaged during transportation. Processing and shipping costs are borne by the company.
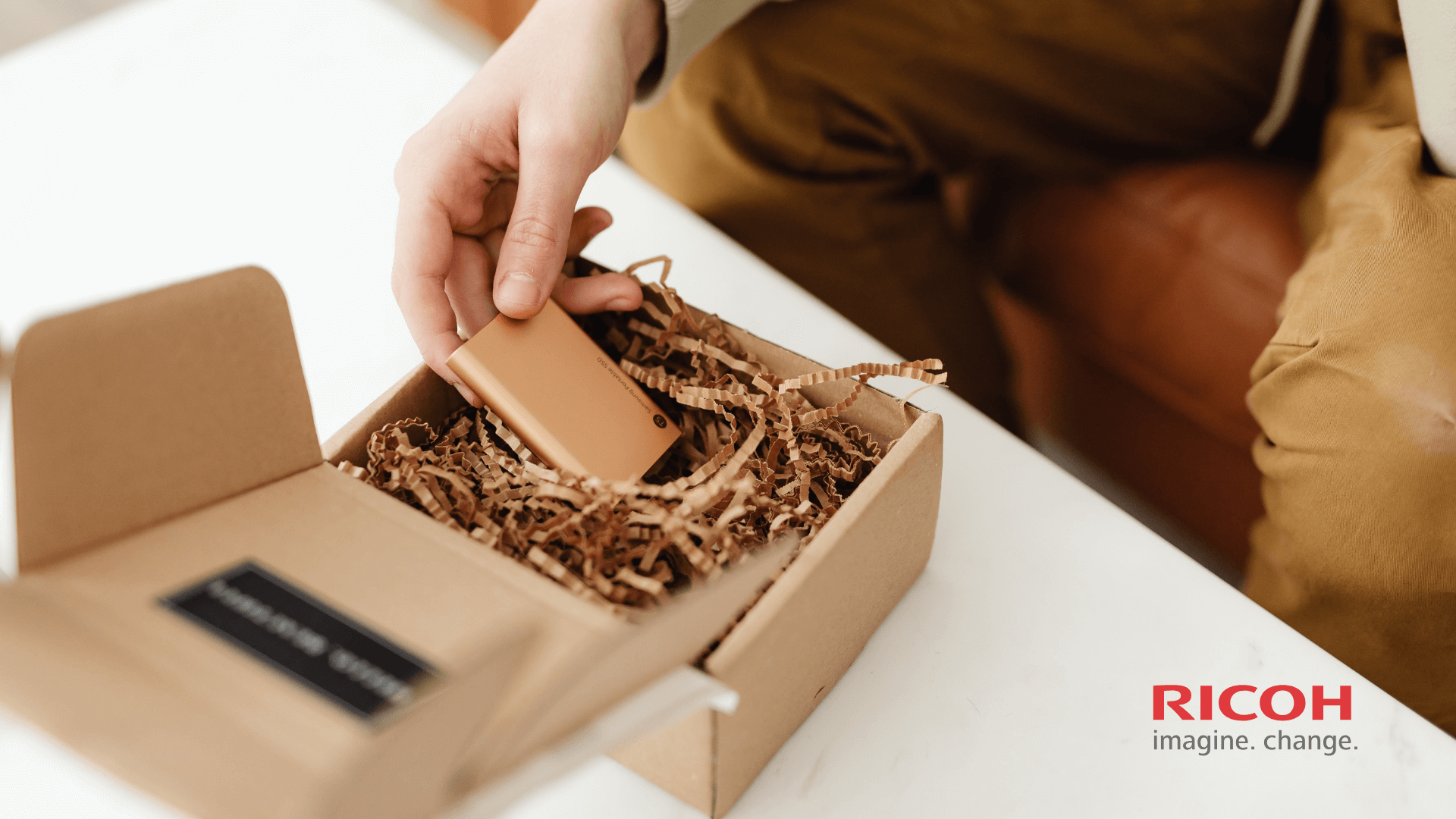 Successful sample testing is the first crucial step toward obtaining UL certification.
Successful sample testing is the first crucial step toward obtaining UL certification.Step 3: Safety Testing and Evaluation
This is the most important step to prove that the product meets UL standards. UL conducts rigorous tests to assess the safety level of the product.
These tests are based on international standards such as ANSI and OSHA regulations. The company will bear all testing costs, including:
- Initial evaluation fee
- Periodic surveillance fee
- UL mark usage fee
- Retesting fee (if applicable)
Step 4: Issuance of UL Certification
If the product passes all tests, UL will issue the official certificate. The company is then authorized to use the UL logo on the product and packaging – a clear indication that the product has met international safety standards.
Note: the UL logo must be printed by a UL-authorized printing facility.
Step 5: Periodic Surveillance
After certification, UL will conduct random or scheduled inspections to ensure the product continues to maintain quality and compliance with standards.
If violations are detected, the UL certificate may be revoked. This process helps preserve the credibility and consumer trust in the product.
7. How to Identify Genuine vs. Fake UL Certification
- Standard UL Logo: The letters “UL” are placed inside a circle, arranged diagonally from left to right, with the “U” higher than the “L.” Below the “U” is the ® (Registered) symbol.
- Canadian Market: If the product meets UL standards in Canada, the logo will appear as cUL or ULC.
- LISTED Text: Below or beside the circle, the word “LISTED” is always written in uppercase letters.
- Control Number: A genuine UL label includes a control number of 4 characters, sometimes 6. This is a key factor in distinguishing genuine UL certification from fake ones.
- Product Information: A genuine UL label always contains identifying details such as the model number, manufacturer’s name, or specific type of equipment.
 A genuine UL mark has sharp lines with easily recognizable symbols (Source: UL Solutions)
A genuine UL mark has sharp lines with easily recognizable symbols (Source: UL Solutions)8. Comparison of UL Certification with CE, RoHS, and FCC
If you have ever seen the CE, RoHS, or FCC logos on devices, you might wonder how they differ from UL certification.
In reality, each certification has its own purpose and scope, and when placed side by side, they help us better understand UL’s role in ensuring product safety and market access.
 Each certification ensures compliance under different product conditions
Each certification ensures compliance under different product conditions
| Certification | Scope of Application | Main Purpose | Common Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| UL (Underwriters Laboratories) | U.S., Canada (cUL / ULC), widely accepted internationally | Ensures electrical, fire, and mechanical safety through independent third-party testing | Electrical devices, electronics, power supplies, household appliances, industrial equipment |
| CE (Conformité Européenne) | European Union | Confirms compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental regulations | Machinery, medical devices, electronics, industrial products |
| RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) | EU and many other countries | Restricts hazardous substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.) | Electronic components, PCBs, electrical and electronic equipment |
| FCC (Federal Communications Commission) | United States | Ensures devices do not cause harmful radio-frequency interference | Phones, laptops, wireless devices, broadcasting equipment |
9. FAQ – Common Questions about UL Standards
1. Is UL mandatory?
Not always. UL is a voluntary certification, but in the U.S., Canada, and the EU, many retailers, distributors, or regulatory agencies require UL certification before products can be sold.
For example, electrical devices, household appliances, and industrial products often need UL certification to demonstrate safety and regulatory compliance.
2. Does the UL mark last forever?
No. UL certification is not permanent. UL conducts periodic factory inspections to ensure that products continue to comply with applicable standards.
If a company changes product design, materials, or production processes, the certification may be revoked or require re-evaluation. UL should therefore be viewed as a continuous compliance process, not a one-time approval.
3. Is UL globally recognized or only regional?
UL is primarily recognized in the U.S., Canada, and the EU. However, as a globally trusted organization, many international customers also accept UL certification as a strong indicator of product quality and safety.
For exports to the EU, CE marking is still required, and other markets may demand additional certifications. UL does not replace all international certifications but serves as a widely respected safety benchmark.
10. Conclusion
UL certification is not just a “safety seal” but also a strategic enabler for international market access, brand credibility, and consumer protection.
Among UL standards, UL 969 – the standard for labels and printed materials – is especially critical for electronics manufacturers, where labels play a vital role in product identification, traceability, and regulatory compliance.
If you are seeking an optimal path to achieve UL 969 compliance, explore the Ricoh UL969 Compliance Enablement Solution Suite.
With over 35 years of experience and deep expertise in supporting businesses to meet UL requirements, Ricoh provides end-to-end support – from documentation preparation, selecting UL Recognized label combinations, conducting testing, through to certification – ensuring peace of mind in exports and sustainable growth.
👉 Discover the Ricoh UL969 compliance enablement solution suite here

Catch Up With UL969 Now
Webinar - From Pitfalls to Smart Compliance: How Vietnamese Factories Win UL Audits
Recommended resources for you

How to Build Collaborative Work Environments for Hybrid Workforces
Unlock the full potential of your workforce. Learn how collaborative solutions can enhance communication, boost productivity, and foster innovation across dispersed teams.

How to Secure Your Digital Workplace from Cyberattacks
Learn how to protect your digital workplace from cyberattacks, safeguarding your data, reputation, and business.

How to Create a Hybrid Workplace That Works
Uncover strategies to build an inclusive hybrid workplace that boosts productivity and engagement.


