What is a Thermal Transfer Ribbon?
Known by many names—thermal transfer ribbon, TTR, barcode ribbon, or simply “ribbon”—this is a specialized consumable used in thermal transfer printing.
It consists of a thin film, typically made from PE or PET, with one side coated with ink. The reverse side, called the backcoat, is not inked and is designed to prevent static buildup and protect the printhead from wear.
Thermal transfer ribbons are used to print information onto labels, most commonly product details or variable data such as manufacturing dates, serial numbers, or barcodes.
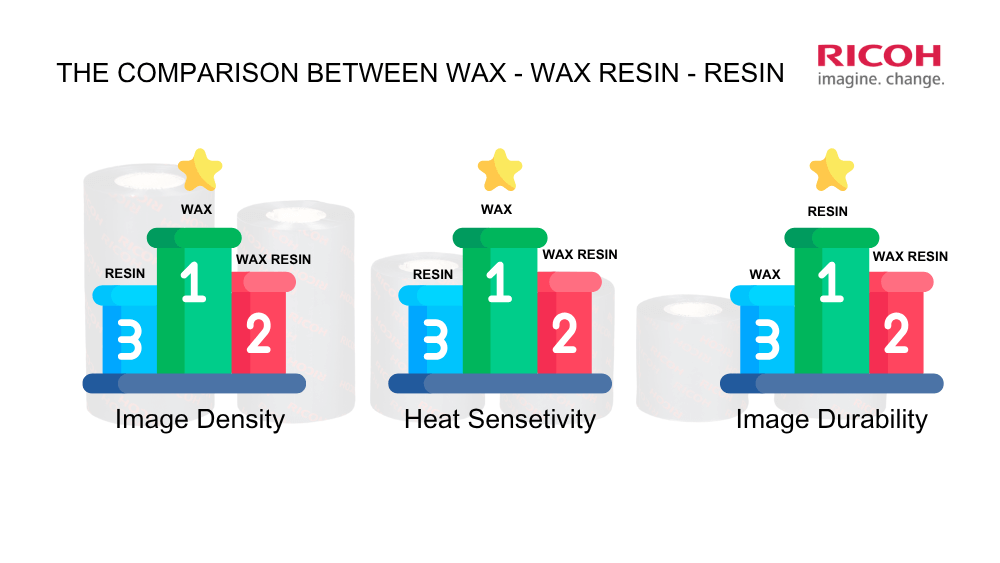
The Three Main Types of Thermal Transfer Ribbons
- Wax:The most economical option, suitable for standard paper labels. Wax ribbons offer lower durability, as the prints can be scratched or faded by heat and chemicals. However, wax provides high darkness and sensitivity, making it a good choice if label durability is not a major concern.
- Wax/Resin:Offers moderate durability, ideal for applications that require some resistance to smudging and light chemical exposure. Wax/resin ribbons strike a balance between darkness, heat sensitivity, and durability—positioning them between wax and resin ribbons in terms of performance.
- Resin:Delivers high durability, suitable for labels exposed to high temperatures, harsh chemicals, or extreme environments. However, resin is not ideal for paper or coated-paper labels, as it may lead to ink smudging or skipping on these surfaces.
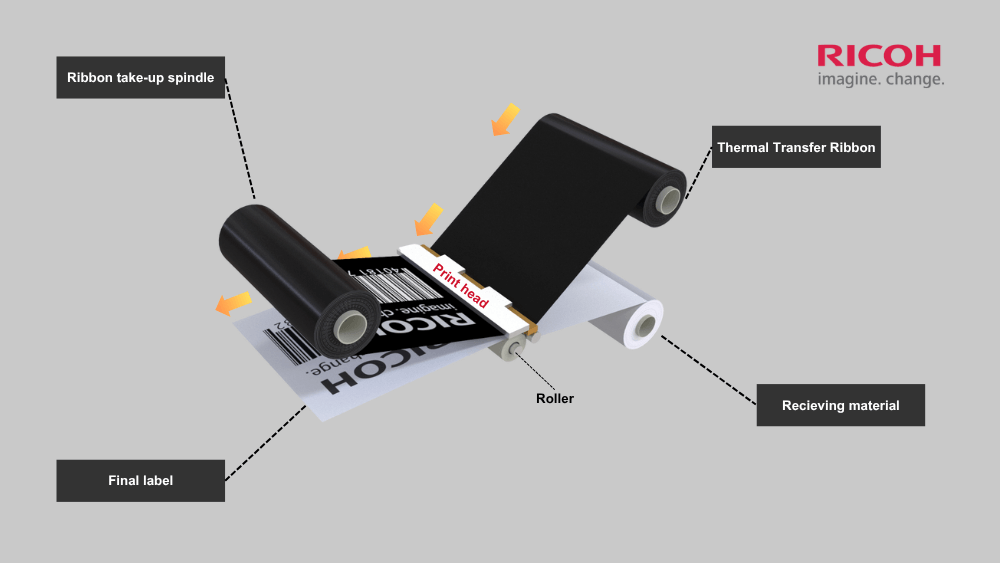
How Thermal Transfer Ribbons Work in the Thermal Transfer Printing Process
When the ribbon is loaded into a thermal printer, the printhead applies heat, causing the ink to transfer from the ribbon onto the surface of the label—creating the printed image.
The process occurs in the following steps:
- Initiation of printing:The thermal printer generates high heat at specific points aligned with the design or data to be printed.
- Interaction between ribbon and label:The ribbon is positioned between the printhead and the label material. As heat is applied, the ink layer on the ribbon melts.
- Ink transfer process:The melted ink transfers directly from the ribbon onto the label surface, bonding tightly to form characters, graphics, or barcodes.
- Completion of the print:After the ink is transferred, the used section of ribbon is rewound onto a take-up spool. This portion cannot be reused, ensuring high precision and consistency for each print job.
Common Applications of Thermal Transfer Ribbons
Thermal transfer ribbons are widely used for label printing in various industries:
- Manufacturing:For labeling components, traceability tags, and product identification on a variety of surfaces including paper, film, and synthetic materials.
- Warehousing & Logistics:For printing labels on cartons, pallets, and storage bins, allowing durable tracking in environments subject to wear and changing conditions.
- Healthcare:For labeling test tubes, medication blister packs, and other items that require resistance to liquids and temperature fluctuations.
- Other industries:For applications where labels must endure high temperatures, chemicals, or friction—resin ribbons are often used to ensure long-lasting print quality.
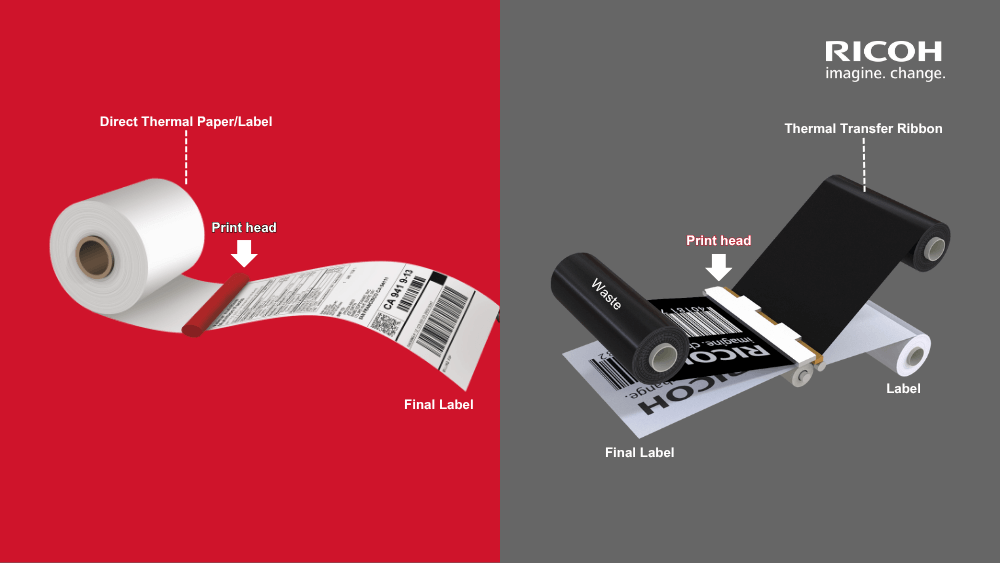
Comparison: Thermal Transfer Printing vs. Direct Thermal Printing
These two printing methods can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
| Criteria | Thermal Transfer (TTR) | Direct Thermal (DT) |
| Printing Principle | Transfers ink from the ribbon onto the label using heat | Image is formed directly on heat-sensitive label material |
| Label Materials | Compatible with a wide range of materials: paper, film, synthetics | Only compatible with heat-sensitive (thermal) label stock |
| Print Durability | High durability – resistant to abrasion, moisture, and chemicals | Lower durability – prone to fading and sensitive to heat |
| Best Use Cases | Ideal for long-lasting labels, long-term storage, and harsh environments | Suitable for short-term use, like tickets, receipts, and temporary tags |
Read our in-depth article comparing Direct Thermal and Thermal Transfer printing methods.
Consequences of Choosing the Wrong Thermal Transfer Ribbon
There are three major risks to using an unsuitable ribbon type:
- Faded or unclear prints:The ink may not adhere properly, resulting in smudging, peeling, or low image quality—especially when exposed to heat, chemicals, or friction during handling.
- Unreadable barcodes:Defective or distorted print images can cause barcode scanning failures, disrupting inventory management and supply chain operations.Increased operational costs:
- Reprinting labels: more frequent printer maintenance, and the risk of non-compliant products reaching the market can all lead to higher costs and potential damage to your brand reputation.
Now you can contact Ricoh for more details about Thermal Transfer Ribbon.

Let’s connect
Get in touch with one of our consultants and find out how we can help you to implement a barcode system
Recommended resources for you
.png)
Things You Should Know About Warehouse Management in 2024
Discover the top trend of warehouse management in 2024

Direct Thermal or Thermal Transfer: Which One To Choose?
This article will provide step-by-step guidance to help you navigate the world of thermal printing technology.

What’s for barcode labels – Thermal or Laser Printing?
Most businesses typically have laser printers for their printing needs within the company. Therefore, most people consider using a laser printer when considering label printing. However, thermal printers specialized for label printing have distinct advantages in terms of printing speed and minimizing issues such as paper jams or adhesive sticking.


